E waste gold recovery is on the rise today. Want to recover 100% precious gold from electronic waste? We are here to guide you! And incase you would like some assistance to guide you through the process, you can get connected with E waste consultants on our platform, to help you earn from waste.
Open your doors for Sustainable Gold.”
Remember early school thought, “Old is Gold”. But now we can say that, “Waste is Gold”. I am talking about electronic devices that have become an integral part of our lifestyle. From mobile phones, tablets, earphones to computers and laptops and many more other electronic devices are found in every single person’s hands. I would say that our life is incomplete without them! Due to advanced technology, every day new electronic devices launch in the market.
Clearly, high speed production of many electronic devices becomes a waste after a few years of use. We all end up throwing these electronic devices into the dustbin. As a result, a heap of e-waste is generated. But now in today’s time, these electronic devices are not considered as waste anymore! We can get many valuable metals from e-waste. And one of the precious metals that can be extracted from the e-waste is Gold.
Yes! In this blog I will talk about gold recovery from e-waste. Are you guys curious to know? So, let’s explore the blog and gain valuable information about e-waste gold recovery.
E-waste Analysis
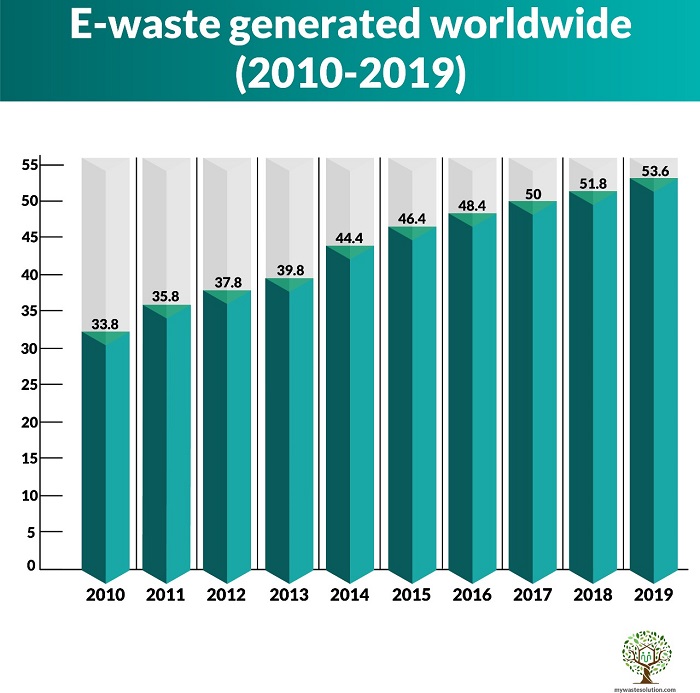
Worldwide mountain of waste electronic and electrical equipment (WEEE) will total an estimated 57.4 million tonnes. Last year’s Global E-waste Monitor 2020 reported that an estimated 53.6 million metric tonnes (Mt) of WEEE was generated in 2019. That represented a 21% jump in the five years since 2014. It is predicted that e-waste will reach 74 million metric tonnes by 2030. Global e-waste generation is therefore growing annually by 2 metric tonnes. It’s about a 3 to 4% increase annually! A major cause of the problem is higher consumption rates of electronics and shorter product life cycle.
You will be amazed to know that;
For 1 million mobile phones that are recycled, the amounts of precious metals that can be recovered are:
16,000 kg of copper
350 kg of silver
34 kg of gold
15 kg of palladium
| Years | Volume of waste generated (in million metric tonnes) |
| 2019 | 53.6 |
| 2018 | 51.8 |
| 2017 | 50 |
| 2016 | 48.2 |
| 2015 | 46.4 |
| 2014 | 44.4 |
| 2013 | 39.8 |
| 2012 | 37.8 |
| 2011 | 35.8 |
| 2010 | 33.8 |
Methods used for E waste Gold Recovery

There are many different methods for Gold Recovery from E-waste. There are mainly three conventional methods. They’re as follows:
Pyrometallurgy
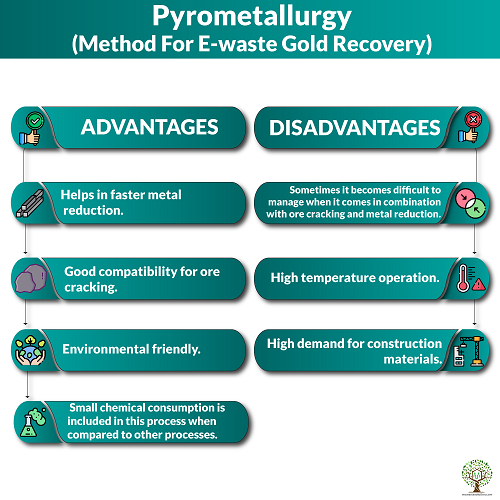
We all know pyrometallurgy is a very important and useful branch of extractive metallurgy.In this process, the gold is needed to crush, encompassing scraps are blazed at higher temperature. By smelting in a plasma arc furnace or blast furnace. Pyrometallurgy is effectively used for recovery of gold from consumed materials. It consists of the thermal treatment of minerals and metallurgical ores and concentrates. It helps to bring about physical and chemical transformations in the materials to enable recovery of valuable metals.
Pyrometallurgical method is found to be economical and eco efficient. If the hazardous emissions from this method are controlled. In fact the method can be used for the segregation and upgrading of the elements followed by hydrometallurgical and electrometallurgical methods of processing. Hence, it is widely used for the recovery of precious metals extracted from the e-wastes. From gold,silver to copper, lead and nickel, each metal can be extracted with the help of advanced technology.
Advantages –
- Helps in faster metal reduction.
- Good compatibility for ore cracking.
- Environmental friendly.
- Small chemical consumption is included in this process when compared to other processes.
Disadvantages –
- Sometimes it becomes difficult to manage when it comes in combination with ore cracking and metal reduction.
- High temperature operation.
- High demand for construction materials.
Hydrometallurgy
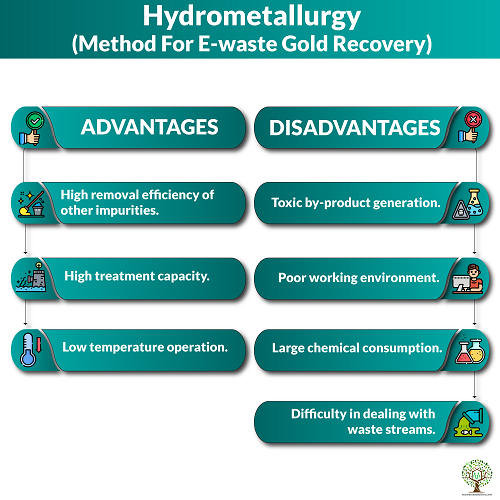
Hydrometallurgy is a well known technique within the field of extractive metallurgy.The process for obtaining metals from their ores is done by hydrometallurgy. It involves the use of aqueous chemistry for the recovery of metals from ores, concentrates,and recycled or residual materials.The main steps in hydrometallurgical processing encompass a sequence of acid or caustic leeches of gold encompassing material. This process is followed by separation and purification procedures. Hydrometallurgical procedure has gained importance all over the world. In fact, the majority of the gold is extracted by this method.
Hydrometallurgical leaching is majorly applied to waste Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) to recover gold from the e-waste. The results show that the Hydrometallurgical recovery of
metals from large pieces of waste PCBs are possible. The HCl took less time for the metal recovery and was thus a very
effective leachant. The best way to dissolve the gold is by using Aqua Regia followed by chemical treatment to get precipitation. Finally the fire assaying technology is an effective way to change the gold powder into pieces of gold.
The purity of gold and the presence of gold and other elements are obtained from Energy Dispersive X-Ray Analysis (EDAX) microstructure .The purity of gold obtained is 23.76K. Percentage of gold in the sample is 99.07%. More over X ray diffraction spectrum of gold and silver also obtained that also indicates 99.35% of gold and 0.65% of silver. Results obtained from the two methods match closely with each other.
In the future with advanced technology, the gold extraction process can be improved to increase the weight of gold extracted from PCB. It can be done by changing the concentration of chemicals, temperature and by using another method. Experiments can be designed for extraction of other elements present in the sample such as copper, silver, zinc,palladium etc. Moreover, the time of precipitation can be increased to enhance the weight of gold recovered.
Advantages –
- High removal efficiency of other impurities.
- High treatment capacity.
- Low temperature operation.
Disadvantages –
- Toxic by-product generation.
- Poor working environment.
- Large chemical consumption.
- Difficulty in dealing with waste streams.
Biohydrometallurgy
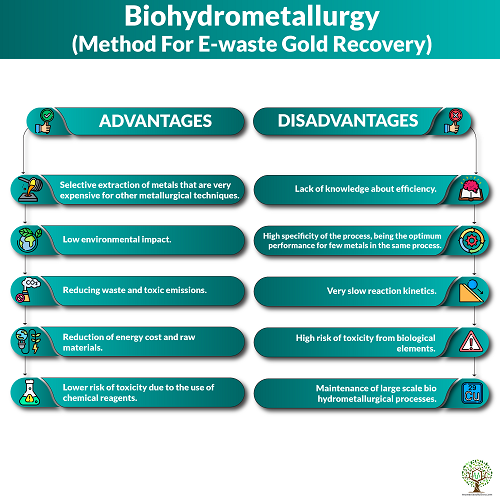
Another best method of gold recovery is by Biohydrometallurgy. It comprises bio oxidation and biosorption. To extract gold from metallic sulphides a bio oxidation method is used. It’s done by the use of bacterially assisted reactions. Most of the gold extraction in industries follow this method. Biosorption procedure is a passive physical-chemical contact. This process amid the charged external clusters of microorganisms and ions in resolution. Living as well as dead organisms can be used. Biosorption procedure has its own advantages such as the process is eco friendly, low cost involved and minimises the chemical or biological sludge. Living and dead biomass that consists of fungi,bacteria, yeast and algae are used to extract gold.
Advantages –
- Selective extraction of metals that are very expensive for other metallurgical techniques.
- Low environmental impact.
- Reducing waste and toxic emissions.
- Reduction of energy cost and raw materials.
- Lower risk of toxicity due to the use of chemical reagents.
Disadvantages –
- Lack of knowledge about efficiency.
- High specificity of the process, being the optimum performance for few metals in the same process.
- Very slow reaction kinetics.
- High risk of toxicity from biological elements.
- Maintenance of large scale bio hydrometallurgical processes.
Besides these conventional methods there are some other ways too from which we can recover gold from e-waste. So let’s have a look at them!
Gold Extraction by Cyanide

Since its introduction into the mining industry during the 1870s, the use of cyanide in gold leaching has been useful. But it is one of the dangerous techniques of metal extraction. This extraction process involves the chemical reaction between the pulverised e-waste and sodium cyanide. This produces a soluble gold cyanide solution that allows for easier extraction of the precious metals. While being useful, gold cyanidation remains a controversial technique, as this technique is prohibited in several countries around the world. Several mining extraction procedures throughout history that have employed this technique have resulted in disastrous cyanide spills that have severely affected the environment.So as cyanide leaching has environmental concerns it is substituted by leaching of gold with thiourea and other leachants that have less environmental concerns.
Advantages –
- Cyanide leaching is very efficient.
- It allows profitable recovery of gold.
- Required less expenditure.
Disadvantages –
- Produce huge quantities of waste.
- Cyanide spills affect the environment severely.
- Cyanide spills into groundwater can persist for long periods of time and contaminate drinking water aquifers.
- Further, cyanide contaminated groundwater can also pollute hydrologically connected neighbouring streams.
Acid Treatment
Acid treatment may sound dangerous to you, but it is one of the easiest way to recover gold from e-waste.The mixture of hydrochloric acid (HCl) and nitric acid (HNO₃) have found to be useful chemicals in the extraction of gold from e-waste. Other mild acids have also been successful in their extraction of gold, as these acids can successfully dissolve gold while limiting their potential to cause adverse effects to the environment.
Advantages –
- High yield expected.
- Faster extraction of gold is possible.
Disadvantages –
- Chemicals are used.
- Acid residues are not disposed of properly, which harms the environment.
Bioleaching
There are many possible alternatives to extracting precious metals such as copper, gold, palladium and silver from e-waste. Microbial processes are one of these methods used over the last decade. Bacteria such as Thiobacillus ferrooxidans and T.thiooxidans, as well as fungi including Aspergillus niger and Penicillium simplicissimum have been documented to successfully extract copper, aluminium, lead and zinc from e-waste. Aspergillus niger and Chromobacterium violaceum are two microorganisms that have been found as suitable and sustainable methods of extracting gold from gold plated electronic devices.
Also, Aqua regia has received a lot of attention in recent years. In the leaching of gold due to its complete dissolution and fast rates. As it is strongly oxidising and corrosive in nature, it is unsuitable for full scale operations. It is a suitable leachant for use in fundamental research. The nitric acid acts as a powerful oxidising agent to form Au3+ ions, while the hydrochloric acid provides a large excess of Cl− ions to form H[AuCl4]. Following are the chemical equations:
Au(s) + 3HNO3(aq) + 4HCl(aq) ⇌ H[AuCl4](aq) + 3NO2(g) + 3H2O(l)
Au(s) + HNO3(aq) + 4HCl(aq) ⇌ H[AuCl4](aq) + NO(g) + 2H2O(l)
As an oxidising acid, HNO3 has been shown to act as a two-stage leachant, selectively dissolving copper, nickel and gold. Initially, a dilute HNO3 (0.1 M) leach step results in suppression of copper leaching but enhanced nickel leaching due to its higher chemical reactivity; increasing the concentration of HNO3 (to 1.0 M) results in high recovery of both copper and gold (98%).
The oxidation of waste Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) using supercritical water (i.e. T > 647 K, P > 218 atm) and sodium hydroxide as a first step. It’s done by following the removal of harmful organic species originating from the degradation of toxic matter such as brominated flame retardants from waste PCBs has been reported. Later on, this process was modified to enhance the leaching of copper along with precious metals such as gold and many others too. In this latter case, HCl was used as the leaching for the initial recovery of copper, followed by iodine–iodide (oxidant and complexing agent, respectively) for subsequent dissolution of the precious metals.
Advantages –
- Cheaper to operate.
- Less maintenance.
- More eco-friendly than other traditional methods.
Disadvantages –
- Slow process when compared to others.
- Sometimes, toxic chemicals are also produced.
Adsorption and precipitation
Adsorption and cementation are prominent techniques for the recovery of gold. It’s make out it’s way from low concentration cyanide solutions, which are derived from commercial mining. Adsorption methods are cheap and simple to operate and typically involve adsorbing the cyanoaurate [Au(CN)2]− on activated carbon particles, which due to their large size can be readily separated from the leach liquor by filtration. From the loaded carbon by heat, the gold is released. It’s done by using a smelter or pH control i.e. on contact with sodium sulphide. These methods are referred to as Carbon-in-Pulp (CIP) methods. Along with this, as other popular variants on this theme Carbon-in-Leach (CIL) and Carbon-in-Column (CIC) methods are also in practice. Cementation methods involve passing the gold leachate solution through a bed of metal shavings or powder. The Merrill–Crowe process uses zinc cementation. In which the filtered cyanide solution is passed through deaerating columns. It’s done to remove the oxygen before adding zinc dust to reduce and precipitate the gold. The precipitated gold is then recovered by filtration, mixed with fluxes (borax, silica, or sodium carbonate) to bind with impurities, and smelted to form bars which are then sent for the further refining processes.
Zn(s) + 2Au(CN)2−(aq) → 2Au(s) + [Zn(CN)4]2−(aq)
The selective recovery of gold (as K[AuBr4]) has been demonstrated through its co-precipitation with α-cyclodextrin. In this process, the insoluble 1D supramolecular polymer:
{[K(OH2)6][AuBr4] (α-cyclodextrin)}n
is formed. In which precise molecular recognition between [AuBr4]− and α-CD occurs. The axial orientation of the anion within the α-CD cavity favours specific second sphere electrostatic and hydrogen bonding interactions between the anion and K(OH2)6+ cation. Life-cycle analysis indicated that application of this technology could significantly reduce the current environmental impact of gold nanoparticle synthesis.
Advantages –
- High performance is shown by this process.
- Easy to maintain and operate.
Disadvantages –
- Adsorbent required regeneration.
- Fire risk from use of organic solvents.
- Volatile organic compounds emissions.
Benefits of gold recovery from e-waste
- The extraction of gold from e-waste greatly reduces the amount of waste that is carelessly deposited into landfills around the world, but it also provides a new recycling opportunity in an environment that desperately needs new sustainable options.
- The innovative technology will reduce up to 50 million tons of e-waste that is dumped into landfills each year.
- If such extraction procedures can reduce the amount of gold that is mined around the world each year.
- Researchers believe a significant reduction in both carbon emissions and other harsh environmental consequences that result from gold mining will also occur.
- The potential for the recovery of gold and other useful metals from e-waste to benefit both the global economy and society at large is unimaginable.
Challenges to overcome
- The reprocessing of waste electronic and electrical equipment (WEEE) is developed all over the world. But,unfortunately the number of wastes accumulated is higher than the number of items reprocessed or recovered.
- You will be shocked to know that many WEEE are shipped to countries like China, Southeast Asia, India and Africa. Many of the items are deposited in open dumps that badly affect our environment and the living conditions of human beings.
- Moreover WEEE contains harmful elements such as lead, mercury, cadmium and Beryllium with hazardous properties.
- So the best way to deal with e-waste recycling is to recover e-waste in which the precious metals are present.
- The e-waste can be extracted and can be used as constituent material of new products. So in this way, the material that needs to be extracted from earth gets reduced. We can help to relieve some of the pressure of the mining industry.
- Reducing mining also reduces pollution, as the mining process has a negative impact on our environment.
E-waste -The Fastest growing industry
Stages of Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment(WEEE) recycling includes collection, storage and transport to the desired locations. This is followed by the processing that includes manual and mechanical processing. The required material is separated,purified and reduced in size. It depends on the desired end use. Later on, they are converted, refined, or otherwise converted to the desired product. In most of the industrialised sectors, the waste is collected at the vicinity of residence. Or else the resident has to hold their WEEE to a central collection point. The initial step of WEEE recovery is the assessment of reuse of the value of it. Some of the components of a computer assembly such as CPUs, recollection chips and drives can be recognized for resale. Whereas other components can be separated into a main physical group that includes plastics, ferrous metals, non ferrous metals, wire and supplementary different components.
For resource and waste management, recycling of e-waste is important. Traditional methods of managing e-waste include disposing in landfills, burning in incinerators. Or exporting to underdeveloped countries. But in the current scenario these processes are not permitted anymore. The presence of precious metals in e- waste makes recycling an attractive and sustainable option. Both in terms of environment and economics, it’s the best solution we can find. So, now take your e-waste and start your journey in e waste gold recovery!


